Example 7.4.7(d): Riemann implies Lebesgue Integrable
Show that the restriction of a bounded continuous function to a measurable
set is Lebesgue integrable.
We should rephrase the question slightly so that it makes sense: suppose
f is a bounded continuous function over an interval (a, b)
and A is a measurable subset of (a, b) with finite
measure. Then f is Lebesgue integrable over A.
First note that if [c, d) is an interval contained in (a, b) then the set f -1 ([c, d)) is measurable, because:
[c, d) =and(c-1/n, d)
f -1 ([c, d)) = f -1 (Since f is continuous, each set f -1 ((c-1/n, d)) is open, hence measurable, and the intersection of measurable sets is again measurable.(c-1/n, d)) =
f -1 ((c-1/n, d))
Now suppose f is bounded by M and fix an integer n. Define the sets
Ej = { xwhere -n(a, b): (j-1)M/n
f(x) < jM/n }
A =
= f -1 ( [(j-1)M/n, jM/n) )A
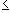 j
j 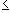 n.
Because of above each set Ej is measurable. Now the
proof can continue just as in a previous exercise,
so we will only sketch it here.
n.
Because of above each set Ej is measurable. Now the
proof can continue just as in a previous exercise,
so we will only sketch it here.
First: Define functions
sn(x) = M/nwhere the sum is taken from j = -n to n. Then the sets Ej are measurable, disjoint, and their union is A, and the functions sn and Sn are simple and integrable.(j-1) XEj(x)
Sn(x) = M/nj XEj(x)
Second: Verify that
(1) sn(x)Third: Finish the proof.f(x)
Sn(x)
(2) I*(f)L
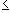
Sn(x) dx and I*(f)L
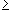
sn(x) dx
(3) I*(f)L - I*(f)L
M/n m(A)
 Interactive Real Analysis
- part of
Interactive Real Analysis
- part of