Theorem 7.1.16: Riemann Integral of almost Continuous Function
If f is a bounded function defined on a closed,
bounded interval [a, b] and f is
continuous except at countably many points, then f
is Riemann integrable.
The converse is also true: If f is a bounded function defined on a closed, bounded interval [a, b] and f is Riemann integrable, then f is continuous on [a, b] except possibly at countably many points.
Proof:
To prove this is not easy; we will start with a simpler version of this theorem: if f is continuous and bounded over the interval [a, b] except at one point xk, then f is Riemann integrable over [a, b].
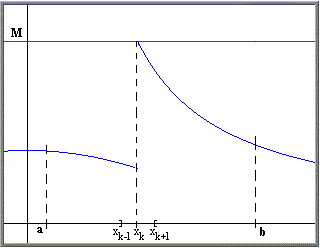 We know that f is bounded by some number M
over the interval [a, b].
We know that f is bounded by some number M
over the interval [a, b].
Take any
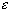 > 0 and choose a
partition P that includes the point xk
such that
> 0 and choose a
partition P that includes the point xk
such that
| P | <Then in particular/ 12M
|xk+1 - xk-1| <We also know that f is uniformly continuous over [a, xk-1] as well as uniformly continuous over [xk+1, b]. Therefore, for our chosen/ 6M
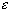 there exists
there exists
- a
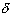 ' such that
|f(x) - f(y)| < 1/3
' such that
|f(x) - f(y)| < 1/3 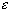 / (b - a)
for all x, y inside [a, xk-1]
with |x - y| <
/ (b - a)
for all x, y inside [a, xk-1]
with |x - y| < 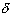 '
'
- a
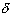 '' such that
|f(x) - f(y)| < 1/3
'' such that
|f(x) - f(y)| < 1/3 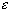 / (b - a)
for all x, y inside [xk+1, b]
with |x - y| <
/ (b - a)
for all x, y inside [xk+1, b]
with |x - y| < 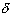 ''
''
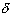 ', and by adding points on the
right side of xk+1 so that the mesh there is
less than
', and by adding points on the
right side of xk+1 so that the mesh there is
less than 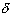 ''. For simplicity,
call that new partition again P. Then we have:
''. For simplicity,
call that new partition again P. Then we have:
| U(f,P) - L(f,P) |For the first term we have: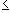
|cj - dj| (xj - xj-1) =
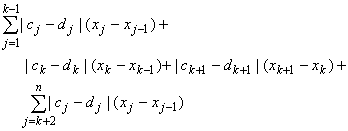
|c1 - d1| (x1 - x0) + ... + |ck-1 - dk-1| (xk-1 - xk-2)because of uniform continuity to the left of xk and our choice of the partition. The third term can be estimated similarly:
< 1/3/(b-a) (xk-1 - x0) < 1/3
/(b-a) (b - a) = 1/3
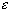
|ck+2 - dk+2| (xk+2 - xk+1) + ... + |cn - dn| (xn - xn-1)Since f is bounded by M we know that |cj - dj| < 2M for all j so that the middle term can be estimated by:
< 1/3/(b-a) (xn - xk+1) < 1/3
/(b-a) (b - a) = 1/3
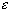
|ck - dk| (xk - xk-1) + |ck+1 - dk+1| (xk+1 - xk)Taking everything together we have:
< 2M (xk+1 - xk-1) < 2M/ 6M = 1/3
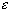
|U(f,P) - L(f,P)| < 1/3Therefore, by Riemann's Lemma, the function f is Riemann integrable.+ 1/3
+ 1/3
=
 Interactive Real Analysis
- part of
Interactive Real Analysis
- part of