Definition 6.1.8: One-Sided Limits of a Function
If f is a function with domain D and
c 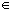 closure(D).
Then:
closure(D).
Then:
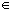 closure(D).
Then:
closure(D).
Then:
- f has a left-hand limit L at c
if for every
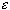 > 0 there exists
> 0 there exists 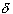 > 0
such that if x
> 0
such that if x 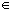 D
and c -
D
and c - 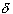 < x < c then
| f(x) - L | <
< x < c then
| f(x) - L | < 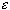 . We write
. We write
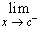 f(x) = L
f(x) = L
- f has a right-hand limit L at c
if for every
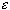 > 0 there exists
> 0 there exists
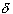 > 0 such that if
x
> 0 such that if
x 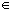 D
and
c < x < c +
D
and
c < x < c + 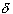 then
| f(x) - L | <
then
| f(x) - L | < 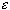 .
We write
.
We write
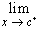 f(x) = L
f(x) = L
 Interactive Real Analysis
- part of
Interactive Real Analysis
- part of