Examples 1.1.2(c):
- E = { x: x = 2n for n
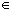 N }
N }
- O = {x : x = 2n - 1 for n
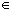 N }
N }
- I = {x
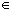 R: x * x = -2}
R: x * x = -2}
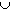 E,
O
E,
O 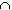 I,
comp(I).
I,
comp(I).
- O
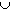 E is the set of all
natural numbers that are even or odd. Hence
O
E is the set of all
natural numbers that are even or odd. Hence
O 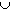 E = N.
E = N.
- O
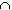 E is the set of all
natural numbers that are both even and odd. Hence
O
E is the set of all
natural numbers that are both even and odd. Hence
O 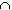 E = 0 (empty set)
E = 0 (empty set)
- comp(I) is the set of all numbers that are not in I. Since I is empty, it is the set of numbers that are not in the empty set. Hence: comp(I) = R (here again the universe is understood to be all real numbers).
 Interactive Real Analysis
- part of
Interactive Real Analysis
- part of