Examples 5.2.7(a):
Consider the collection of sets
(0, 1/j) for all j > 0. What is the intersection of
all of these sets ?
The intersection of all intervals (0, 1/j) is empty. To see
this, take any real number x. If
x 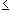 0
it is not in any of the intervals (0, 1/j), and hence not
in their intersection. If x > 0, then there exists an
integer N such that 0 < 1 / N < x. But then
x is not in the set (0, 1 / N) and therefore
x is not in the intersection. Therefore, the intersection is
empty.
0
it is not in any of the intervals (0, 1/j), and hence not
in their intersection. If x > 0, then there exists an
integer N such that 0 < 1 / N < x. But then
x is not in the set (0, 1 / N) and therefore
x is not in the intersection. Therefore, the intersection is
empty.
Note that this is an intersection of 'nested' sets, that is sets that are decreasing: every 'next' set is a subset of its predecessor.
 Interactive Real Analysis
- part of
Interactive Real Analysis
- part of