Divergence Test
If the series
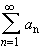 converges, then the sequence
converges, then the sequence
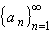 converges to zero. Equivalently:
converges to zero. Equivalently:
This test can never be used to show that a series
converges. It can only be used to show that a series diverges.
Hence, the second version of this theorem is the more important,
applicable statement.
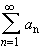 converges, then the sequence
converges, then the sequence
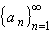 converges to zero. Equivalently:
converges to zero. Equivalently:
If the sequence
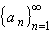 does not converge to zero, then the series
does not converge to zero, then the series
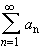 can not converge.
can not converge.
Proof:
Suppose the series does converge. Then it must satisfy the
Cauchy criterion. In other words, given any
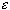 > 0 there exists
a positive integer N such that whenever
n > m > N
then
> 0 there exists
a positive integer N such that whenever
n > m > N
then
|Let m > N and set n = m. Then the series above reduces to| <
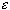
| a n | <if n > N. That, however, is saying that the sequence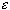
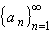 converges to zero.
converges to zero.
 Interactive Real Analysis
- part of
Interactive Real Analysis
- part of  converges or diverges ? How about convergence or divergence of
the series
converges or diverges ? How about convergence or divergence of
the series
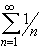 ?
?