Theorem 4.1.9: Cauchy Criteria for Series
The series
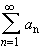 converges if and only if for every
converges if and only if for every
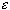 > 0
there is a positive integer N such that if
m > n > N then
|
> 0
there is a positive integer N such that if
m > n > N then
| 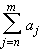 |
<
|
<
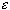
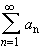 converges if and only if for every
converges if and only if for every
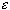 > 0
there is a positive integer N such that if
m > n > N then
|
> 0
there is a positive integer N such that if
m > n > N then
| 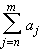 |
<
|
<
Proof:
Suppose that the Cauchy criterion holds. Pick any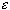 > 0. Then
> 0. Then
| S n - S m | = |But that means precisely that the sequence of partial sums { S N } is a Cauchy sequence, and hence convergent.| <
Now suppose that the sum converges. Then, by definition, the
sequence of partial sums converges. In particular, that sequence
must be a Cauchy sequence: given any
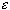 > 0, there is
positive integer N such that whenever
n, m > N we have that
> 0, there is
positive integer N such that whenever
n, m > N we have that
| S n -S m | = |But that, in turn, means that the Cauchy criterion for series holds.| <
 Interactive Real Analysis
- part of
Interactive Real Analysis
- part of