Convert the following numbers into the indicated coordinates and draw them in the complex plane:
- Prove that if z = r cis(t) then
= r cis(-t)
Example 1.2.11 (c): Polar coordinates examples |
Convert the following numbers into the indicated coordinates and draw them in the complex plane: |
If z = r cis(t) then we have in rectangular coordinates that z = x+iy with
x = r cos(t)
y = r sin(t)
But the vector r cis(-t) has coordinates
r cos(-t) = r cos(t) = x
r sin(-t) = -r sin(t) = -y
because cos is even and sin is odd. Thus
r cis(-t) = x - i y = 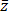 .
.